News Desk
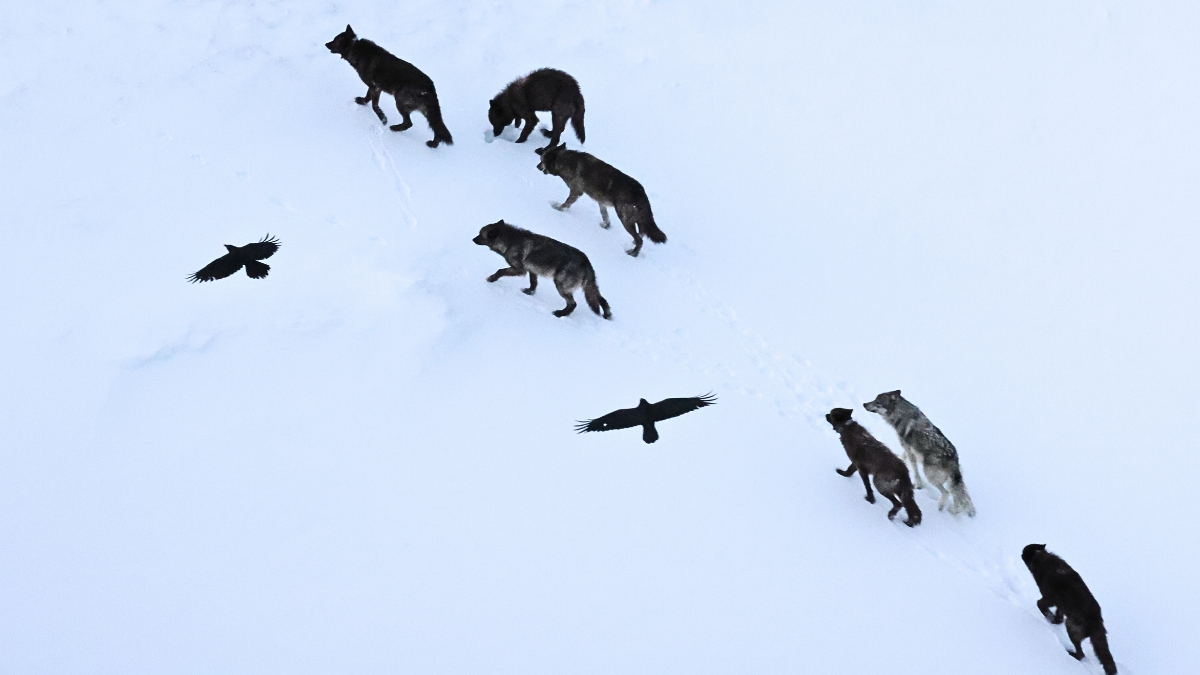

The partnership between ravens and wolves goes back to Norse mythology – Odin’s birds scouted ahead and led prey to the god’s canines, a relationship that provided food for all. The myth has some roots in reality: when wolves have a successful hunt, ravens are often observed first on the scene – and new research published Thursday in the journal Science put the legend to the test.

A new study, published in JAMA Network Open, reports the outcome of a clinical trial out of Johns Hopkins University assessing the effectiveness of psilocybin as a treatment for smokers attempting to quit. The trial compared the effectiveness of one dose of the “magic mushroom” drug to months of the common nicotine patch, combined with cognitive behavioral therapy in both groups. The results might push psilocybin into the limelight as a more effective addiction treatment.
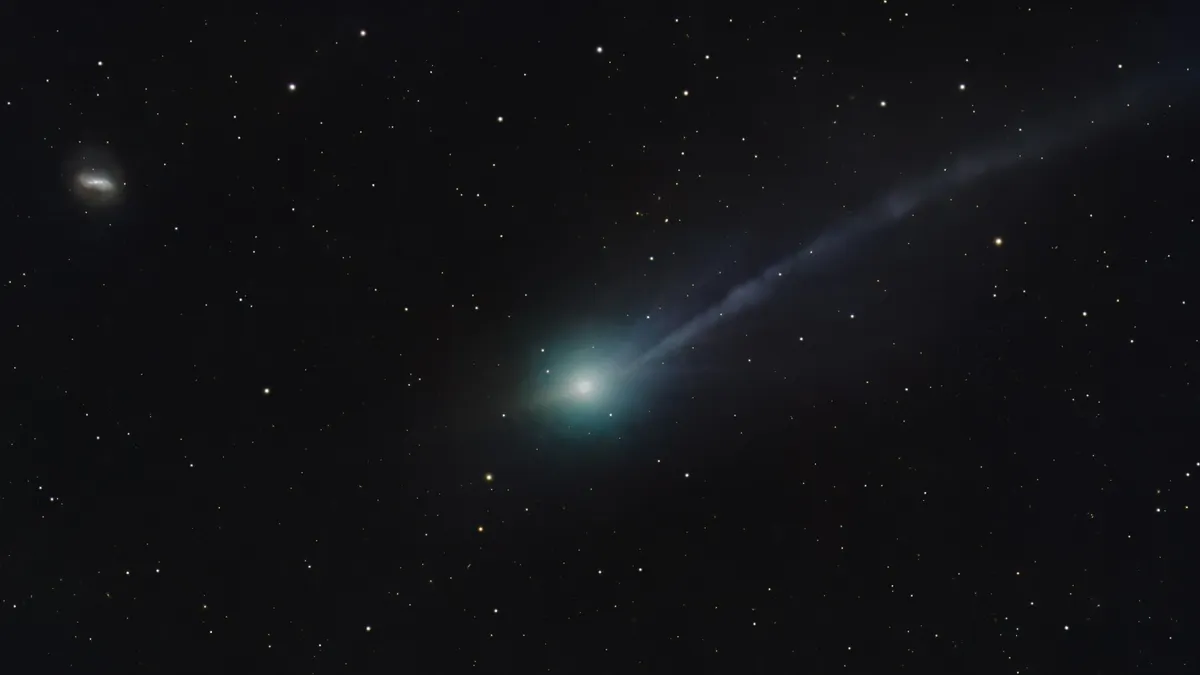

The comet formed in a cold and distant part of the early Milky Way up to 12 billion years ago, potentially putting it just under 2 billion years the age of the universe.

In a study published in the journal Iran, researcher Gad Barnea has uncovered new evidence suggesting that Zoroastrian religious practices were more prevalent and left a deeper imprint on surrounding communities than previously recognized.
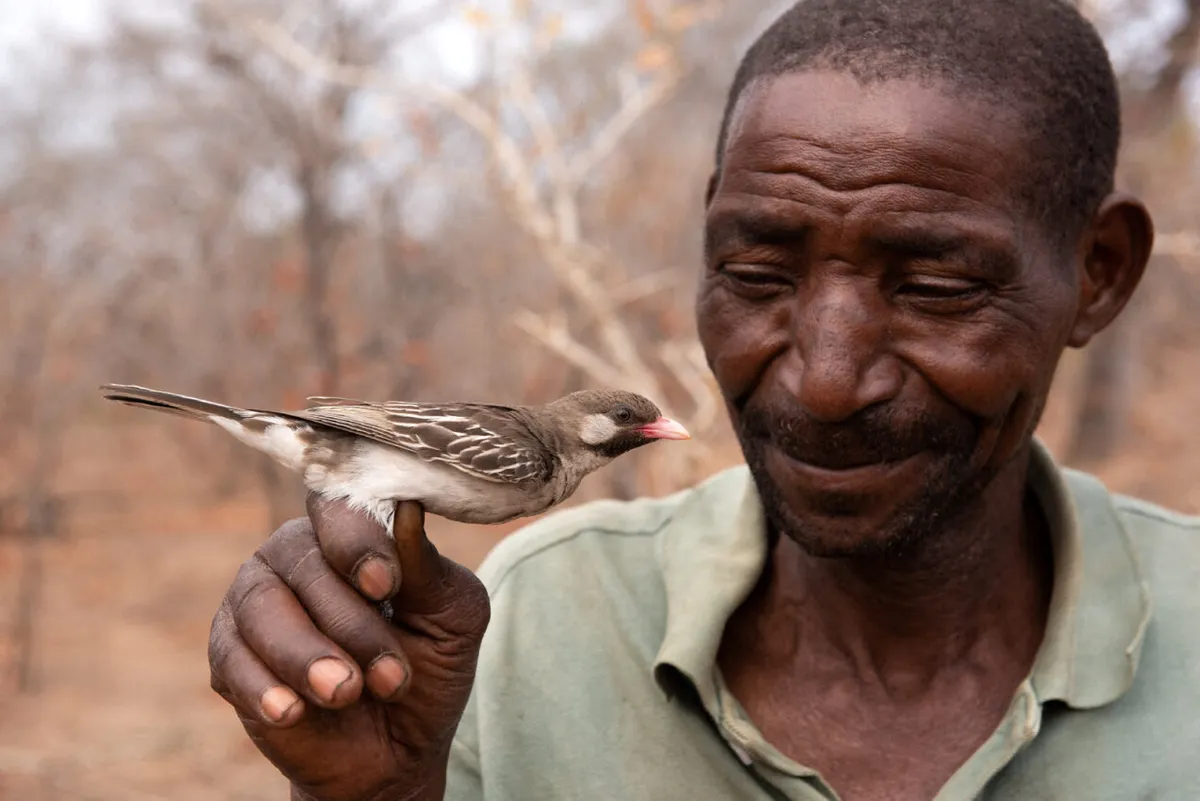

In his new book, “The Call of the Honeyguide: What Science Tells Us About How to Live Well With the Rest of Life” (Hachette Book Group, 2025), Rob Dunn, a professor of applied ecology at North Carolina State University, explores these complex interdependencies found across the natural world, including the numerous mutualisms humans engage in, such as our relationships with dogs and with the microbes in our guts.

Two researchers discuss how ancient DNA is used to track how people moved and lived during Britain’s Bronze Age. The new paper, produced with colleagues from the U.S. and across Europe, has highlighted some of the more complex interactions between ancient populations that took place in north-west Europe.

Comet 3I/ATLAS continues to make astonishing headlines, thanks to new findings from astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA). This new research reveals that 3I/ATLAS is packed with an unusually large amount of the organic molecule methanol—more than almost all known comets in our own solar system. The findings are posted on the arXiv preprint server.
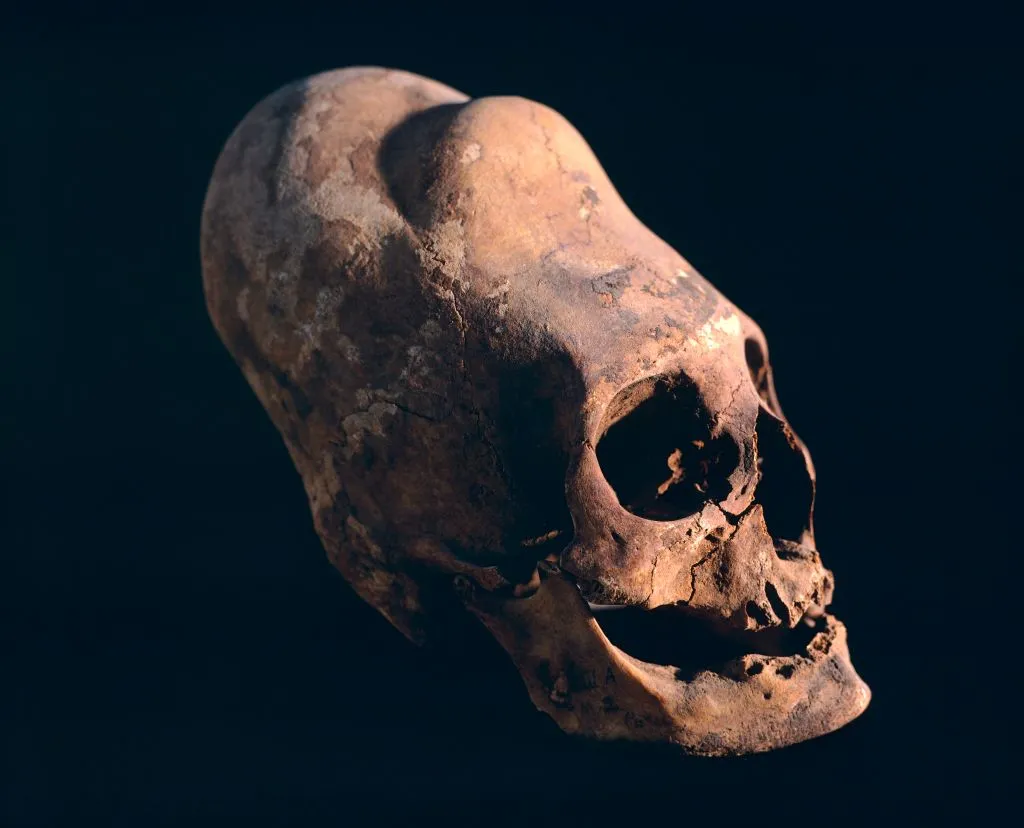

When the Spanish first reached the Andes, they found something surprising: Many of the locals had long, pointy heads. They discovered that the Collagua, an indigenous group in Peru that was conquered by the Inca, had a practice of shaping the head starting in infancy, before the skull bones fused and soft spots disappeared.
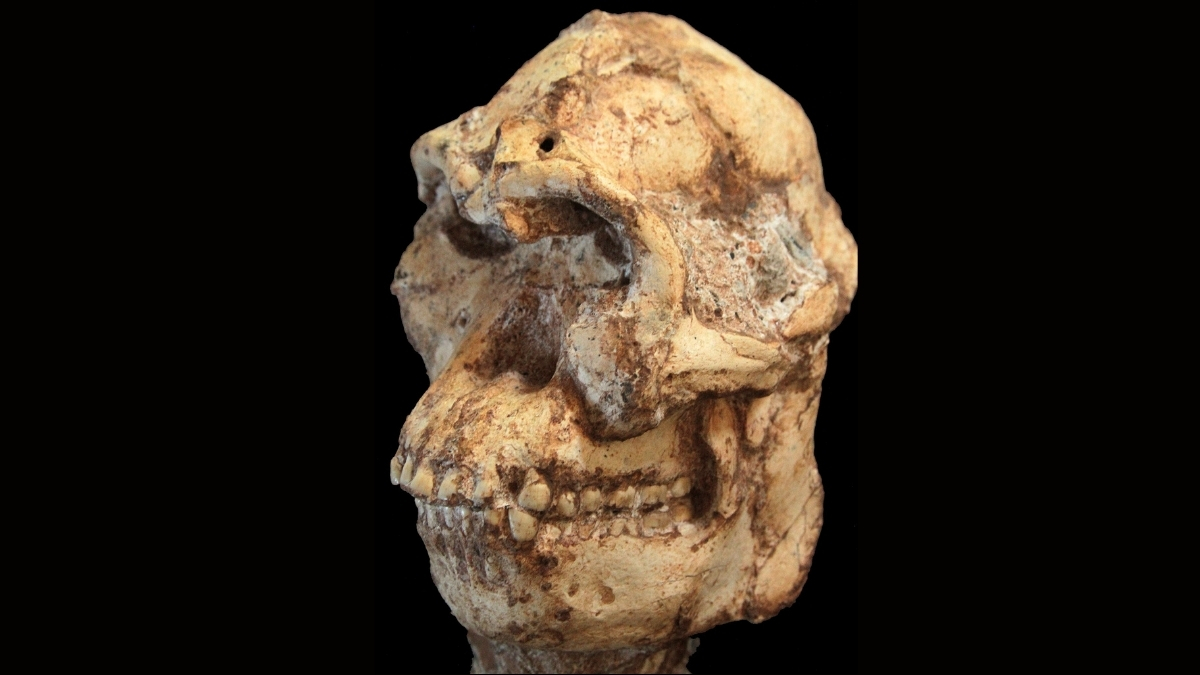
A new study, led by paleoanthropologist Amélie Beaudet at the Université de Poitiers in France, has now digitally pieced together Little Foot’s face for the first time. The research was published in the journal Comptes Rendus Palevol.

Thousands of years ago, European communities used a variety of plant and animal products to create elaborate meals, according to a study published in the open-access journal PLOS One by Lara González Carretero of the University of York, U.K. and colleagues.
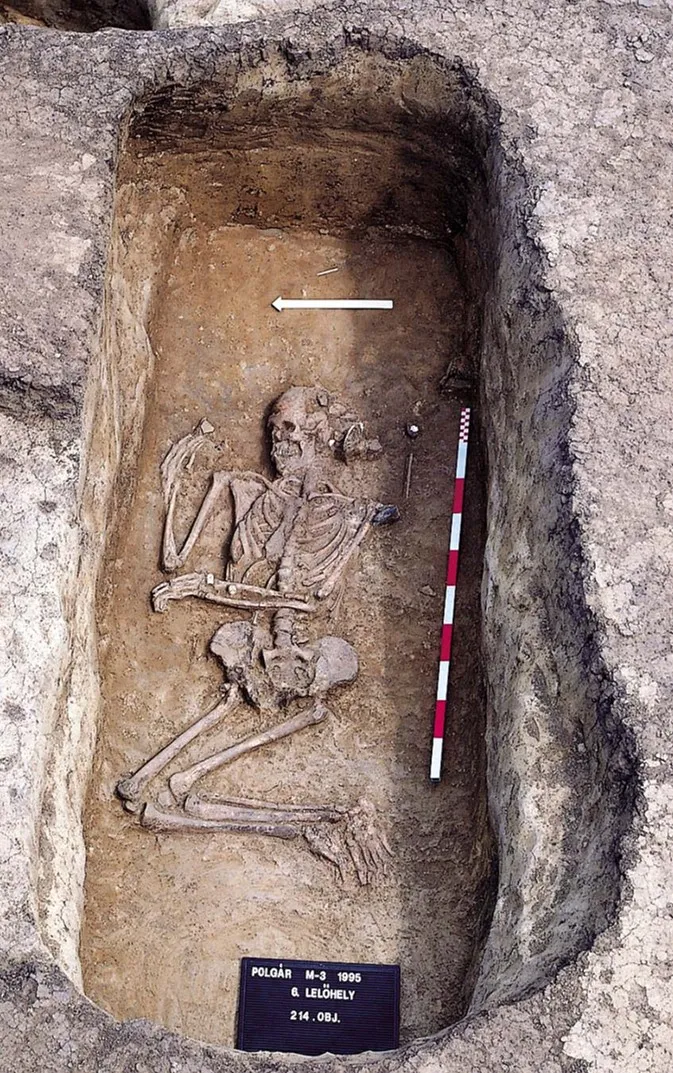

A Stone Age woman buried with male-associated artifacts in what is now Hungary is revealing that her society embraced complex identities and flexible gender roles 7,000 years ago, a new study finds. In the study was published Feb. 16 in the American Journal of Biological Anthropology.
A recent study published in Communications Biology suggests that a powerful psychedelic drug can induce a unique brain state where awake and moving animals exhibit brain waves typically associated with deep sleep. This unusual blend of sleeping and waking characteristics provides evidence that psychedelics may temporarily reorganize brain activity in ways that promote learning and emotional recovery.

Unretouched triangular microlithic projectile points have been identified from their impact traces in the oldest occupation layers of the Obi-Rakhmat site in Uzbekistan, dating to 80,000 years ago…This new study, published in PLOS One journal, provides a strong argument that could rewrite history on Homo sapiens’ first settlement in Europe.

A new paper published in Nature (11th Feb) has highlighted some of the more complex interactions between ancient populations that took place in north-west Europe. The research untangles the origins of prehistoric populations across Belgium and the Netherlands, as well as identifying the source population for a migration into Britain during the late Neolithic that seems to have led to a 90% replacement of Britain’s Neolithic farmers.
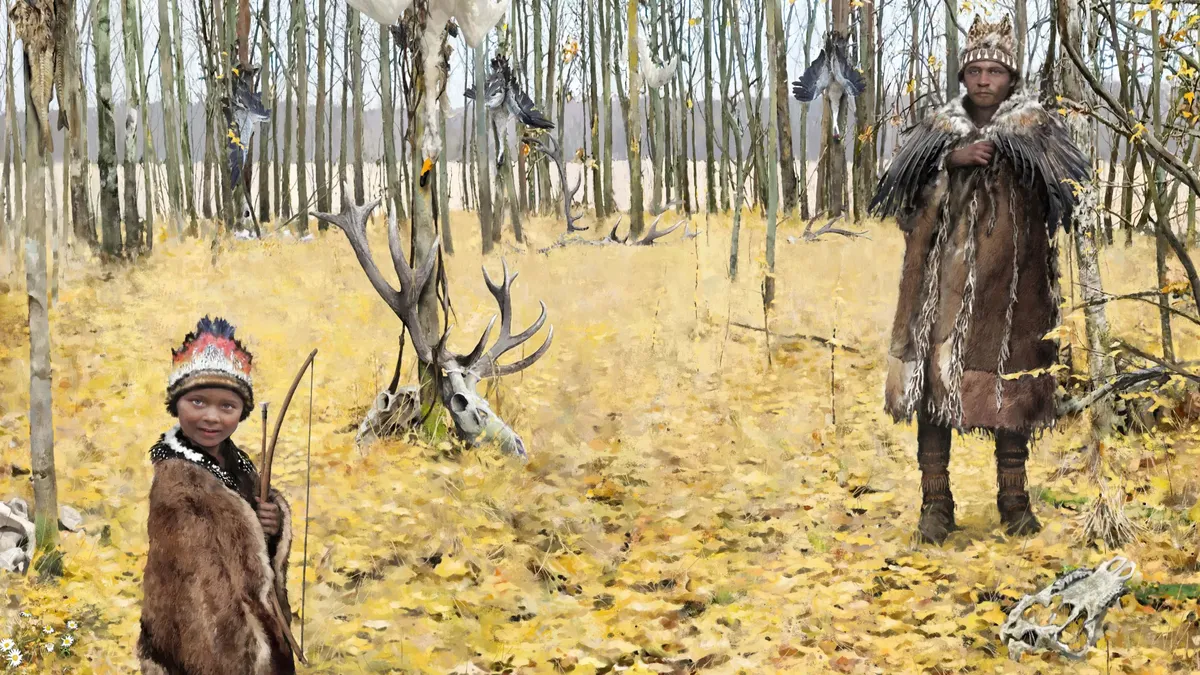

A new method of studying the contents of soil samples has revealed Stone Age people in Sweden were buried in decorated fur-and-feather clothing. In the study, published Feb. 20 in the journal Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, Kirkinen and colleagues detailed the evidence of perishable materials that they found in 35 burials at Skateholm…

Six planets are linking up in the sky at the end of February, and most will be visible to the naked eye. It’s what’s known as a planetary parade, which happens when multiple planets appear to line up in the sky at once.








